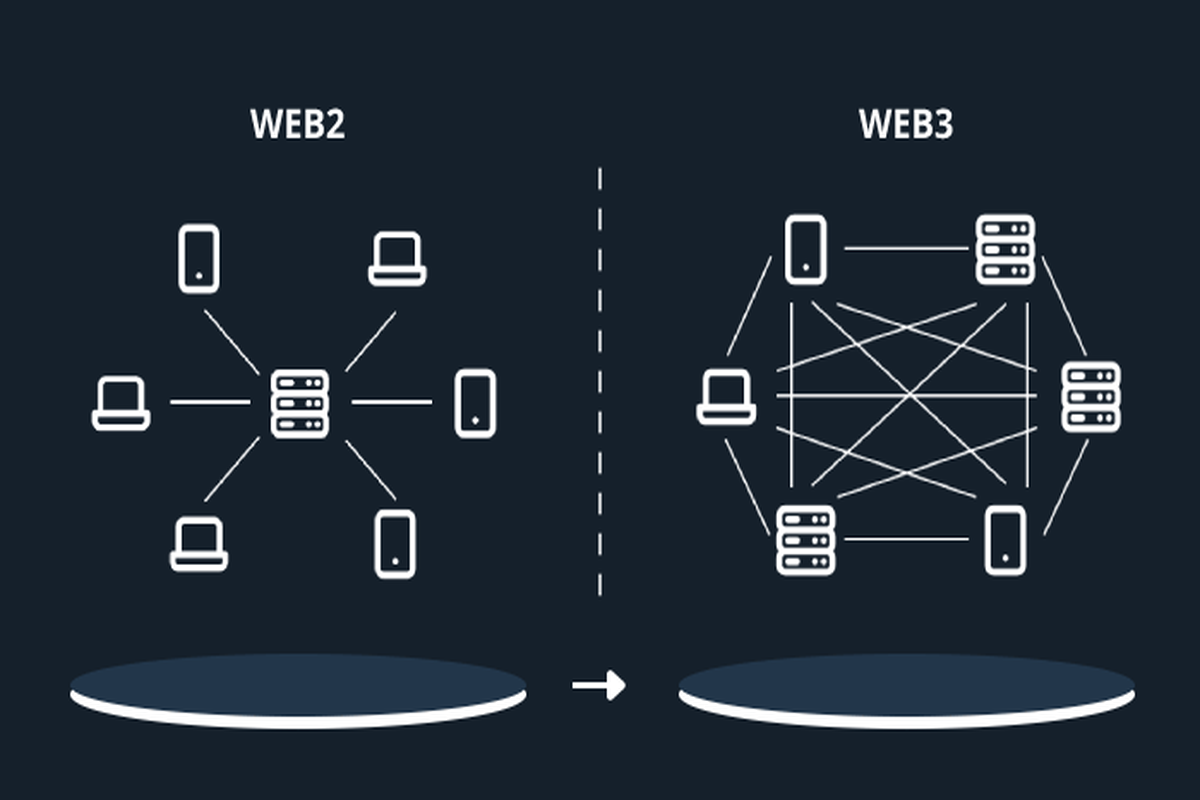
Web3 is a decentralized, trustless, and permissionless ecosystem that takes control from a centralized entity and gives it to a pool of participants. On the flip side, Web2 is a centralized space that is dominated by firms like Microsoft, Google, Facebook, and others.
Notably, Web3 is described as the next generation of the internet that is decentralized. Hence, it is fundamentally different from Web2, which is a centralized ecosystem majorly influenced by a client-server model.
In Web2, the backend code that powers applications gets deployed onto a server hosted by platforms like the Amazon Web Service (AWS) or Google Cloud. The system centralizes the power and the companies are called Big Tech. They can block access to anybody or Exchange users’ critical data for money.
Related: What Is Decentralized Social (DeSo) And How Does It Work In 2022?
Nevertheless, the infrastructure of Web3 is mainly designed to take away this advantage from Big Tech and decentralize it, facilitating innovation, increasing transparency, and providing users with absolute control over their data and online interactions. There is no server or client in Web3. Instead, there is peer-to-peer file sharing powered by the Interplanetary File System (IPFS).
Although Web3 applications are trustless and permissionless, some of the private blockchains need permission. “Permissionless” is the capacity of smooth inter- and intra-platform communication, while “trustless” describes the characteristic where the users have to trust the network and not the participants. On the contrary, Web2 applications need approval by the centralized authority and users’ trust to remain functional.
Can Web3 Resolve The Challenges Of Web2?
Web3 strives to return content rights to the author, boost security levels, get rid of unfair and unwanted censorship, automate software functions, increase transparency, and support a creator economy.
Due to the characteristics of Web3, businesses can take advantage of opportunities that are beyond imagination. Concepts like decentralization and permissionless cybersphere were only in sci-fi. Nevertheless, Web3 aims to resolve the problems in Web2, paving the way to a decentralized era within the internet.
Data Ownership
Decentralization puts bigger control in the hands of users, ending the monopoly of Big Tech. Users can decide whether they would like to share their data with everyone or keep it private. Since computing power and decision making is highly diversified, the system becomes inherently more stable than the centralized networks. The entire operation in the centralized systems is concentrated on a cluster of servers and a core decision-making entity or person.
Although many Web2 applications have moved toward multi-cloud hosting, the resilience of projects that are highly decentralized in real terms is just at another level. Enterprises can choose a topography for their application subject to their data landscape and the challenges they wish to address.
Data Security
Data stored in a massive centralized database is extensively vulnerable. Hackers only need to break through one system to compromise all the valuable and private user data. Mostly, insiders tip key information to external cybercriminals. Decentralized systems are designed to become resistant to the behavior of some participants, making security in Web3 highly efficient than Web2 networks in keeping user data secure.
On the other hand, when nearly all firms are going digital and data-driven, the risk of malicious attacks has also increased exponentially. In such circumstances, vandalism in cyberspace has become a major threat. Already, it appears to be threatening monetary and reputation loss. Decentralization boosts security levels as it strives to eliminate existing issues.
Unfair Censorship
Centralized networks mostly subject users to unfair censorship. Decentralization allocates the authority to the participants which makes it nearly impossible for any centralized entity or individual to influence a narrative that does not suit them.
A Web2 social media site like Twitter, for example, can censor any tweet at any given time they want. On a decentralized Twitter, the tweets will be uncensorable. Furthermore, payment services in Web2 may restrict payments for particular kinds of work.
In Web3, censorship will be quite hard, for participants with great intent and malicious players. Decentralized web promises control and privacy to all the participants. Also, network participants can adopt an active role in the governance of the project by casting votes.
Financial Freedom
In Web3, each participant is a stakeholder. Backed by an array of technologies that inherently resist control, Web3 promotes financial freedom. Decentralized finance (DeFi), where anybody can readily engage in financial activities, is a great example of the independence that the participants enjoy.
Notably, complying with Anti-Money Laundering (AML) and Know Your Customer (KYC) regulations open decentralized finance to new user groups resulting in mass adoption. Furthermore, payments in Web2 are made in fiat, while Web3 payments are made via cryptos, although fiat payment networks can be integrated too.
Related: Money Laundering In Banks And Cryptocurrencies, Which Is Safer?
Transparency
Transparency is something that is integrated into the design of decentralized networks. Nodes work concurrently to guarantee the seamless operation of the network and no node can make decisions in isolation. Even the other participants have a role in decision-making about governance via the casting of votes.
Web3 transactions are mainly irreversible and traceable, therefore ruling out any possibility of somebody making changes in the database post-transaction. That makes Web3 a powerful tool against fraudulent behavior.
Automation
Smart contracts automate the network that can work without any human intervention. The code reflects the agreement between different stakeholders, executing transactions that can never get reversed. Smart contracts majorly bring down operational costs, make transactions highly secure, and get rid of prejudice.
Projects, nonetheless, need to be careful about the vulnerabilities that exist in smart contracts code that hackers can benefit from stealing the booty. It can be overcome by getting the smart contract code majorly audited by a team having a proven track record in vulnerability assessments using a mixture of automated and manual tooling.
A Web3 example of speeding up automation is Zokyo, which mainly specializes as an end-to-end security resource for blockchain-based projects.
Creator Economy
Nonfungible tokens (NFTs), a component of the Web3 ecosystem, have added another notable dimension to the web economy. The tokens make every digital asset distinct in some sense. Irrespective of the number of times it gets duplicated, there is a perfect way to distinguish it.
The feature is useful to safeguard the assets against online forgery and maintain the exclusive rights of the owner over their digital assets. In Web3, nonfungible tokens may serve as metaverse assets, certification, and game assets, opening up unlimited possibilities and empowering content creators to make money in an unexpected manner.
Related: Web3 – An Ultimate Guide for Beginners
Earlier, when the audiences consumed the content of a developer, the audience just had the emotional or intellectual benefit. With the inception of NFTs, developers can now turn their community members into investors and offer them some tangible value out of that interaction.
For example, in case somebody has launched a group on a decentralized social media platform, the first 50 subscribers may get rewarded with some redeemable NFTs in case they spend a specific amount of time interacting there.
On the opposite of what many think, one does not have the technical know-how to develop an NFT-based economy. There are no code solutions like NiftyKit available for different development needs like building revenue splits, NFT smart contracts, token gating, embeddable SDKs (software development kits), and a lot more. Without any form of coding, one can start setting up a creator economy.
How Web3 Resolves Interoperability Problems
For speeding up the acquisition of users and gaining relevance, integrating Web2 with Web3 is as crucial as Intra-Web3 communication. Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is an advanced technology that assists in addressing these worries by facilitating interoperability between blockchains.
‘Cross interaction’ or interoperability is an important feature in computer networks that facilitate smooth data exchange between Web2 and Web3, and within Web3 projects. One example of the feature is Twitter unveiling NFT profile pictures for Twitter Blue (checkmark) subscribers for iOS in January 2022.
The users can validate the ownership of the NFT by integrating their Twitter profile with the wallet storing the NFT. To activate data exchange, as it happened in the Twitter feature, the engineers integrate Web2 platforms with Web3.
Intra-Web3 communication is also important for the effective functioning of digital applications. Owing to the Ethereum blockchain that hosts most of the dApps in Web3, being compatible with EVM is a critical requirement for any project that needs to be made interoperable. EVM functions as the runtime environment for smart contracts in the Ethereum blockchain.
Related:Alex Shevchenko- Aurora Labs CEO talks to us about NEAR’s Ethereum Virtual Machine
Blockchains operate in isolation and require solutions like sidechains to link with other chains. By description, a sidechain is a blockchain that runs independently of the host blockchain or mainnet via a 2-way bridge. Notable examples of sidechains are Polygon PoS and Gnosis Chain (formerly xDAI).
Horizen blockchain is another example of a sidechain project that is building a platform that will be wholly compatible and interoperable with Ethereum, opening up its massive node infrastructure to the general Ethereum community and enabling businesses to develop solutions rapidly. They are also now exploring the possibility of adding an EVM layer on other blockchain networks to support greater interoperability for the users to benefit from multiple ecosystems.