Polygon (MATIC) is described as a layer 2 solution that boosts Ethereum and powers its scalability. In that context, the Polygon network is a complete and fully functional multi-chained system, an infrastructure, and a protocol.
The protocol links Ethereum-compatible blockchain networks and is well-designed to solve the scalability challenges that exist on the current Ethereum network. It works on top of Ethereum’s primary blockchain. The network utilizes side chains to unclog the underlying platform smartly and cost-effectively.

Polygon’s multi-chain network provides an infrastructure for supporting blockchain platforms to communicate with one other without needing to involve Ethereum’s primary chain. Nonetheless, the network retains Ethereum’s interoperability, liquidity, and security.
At first, Polygon was known as the Matic Network described primarily as a scaling solution for Ethereum. In 2019, Matic hosted its token sale on the Binance Launchpad at a time when the Initial Exchange Offerings (IEO) were becoming popular.
Although it is designed to function optimally and enhance Ethereum operations, Polygon has encountered several challenges recently.
Related:A Deep Dive Into The Polygon Network
Polygon Suffered Multi-Hour Outage After Node Halts
Recently, Polygon suffered a multi-hour outage arising from an issue with one of its nodes. On March 10, Polygon said that its network had been affected by downtime from 5:50 pm UTC due to its Heimdall node halting. The next transaction was successfully processed by the network over eight hours later as of 2 am UTC on March 11.

The Polygon developers explained that the Heimdall node is primarily used by one of the two layers of its Proof-of-Stake (PoS) chain for all the transactions that are associated with bridging and validators. Polygon boldly attributed the node’s outage to another minor upgrade implemented earlier to the network’s state bridging module.
Polygon commented:
“We suspect there may have been a bug in the upgrade which affected consensus, and caused different Heimdall validators to be on different versions of the chain, thereby not reaching 2/3 consensus.”
They also said that the Heimdall node will stop operating by design when consensus is not achieved. Nevertheless, the developers strived to identify the “definitive cause” for the outage, together with “mitigation solutions that will resume operation as soon as possible.”
Despite that outage, Polygon insisted that all user funds and data are entirely safe.
Disgruntled Users
Following the outage, Polygon’s Twitter was bombarded with complaints from users who tried to transact in the network while unaware of the issue. Many of these users reported failed transactions on the Polygon deployment of OpenSea where their wallet balances failed to update. That delay in updating made it seem like funds were lost.
While transactions were just stuck in the queue, scammers appeared to have been contacting affected users disguising themselves as members of the Polygon support team.
Guys can you tell me if this is legit? I really don't trust on crypto space… Sorry for my laughing, but it's just hilarious somebody to reach you asking for your wallet…
— Willi Goen (@willigoen) March 10, 2022
Twitter user ‘WeRyoshi’ warned:
“Watch out for scammers.”
The commenter also alleged that they had been waiting for more than 15 hours for their transaction to complete. In the wake of that outage, NFT project Courtyard was compelled to delay its public mint by 4 hours. Recently, Polygon copped flak for suffering many outages since the beginning of this year.
In February, transactions were suspended due to a gas-station outage. Before that, an issue with gas estimation caused users to have no access to transact using nonfungible tokens (NFTs) on the network for many days in January.
Gas Fees On Polygon More Than On Ethereum
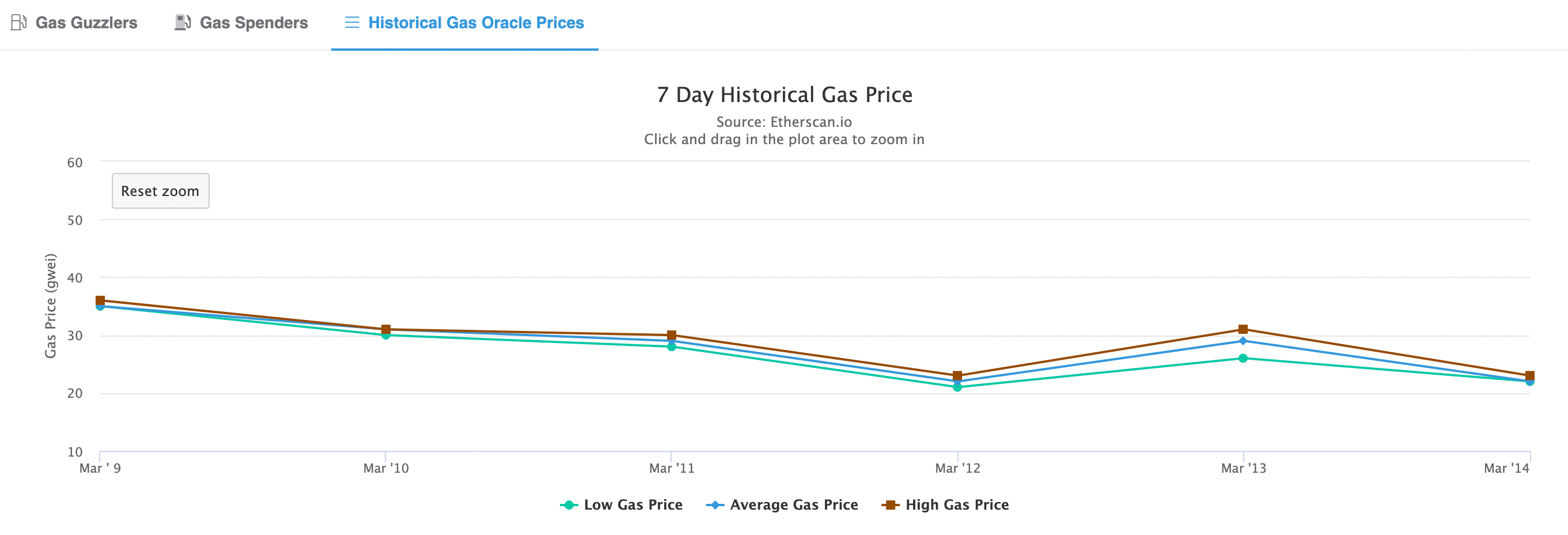
On March 14, gas fees were as low as 10 gwei on Ethereum’s layer-1 making it a bargain deal even when compared to the Polygon sidechain. Notably, Ethereum gas fees are now at their lowest since July 2020.
Who would have thought that Ethereum gas fees would be cheap again? In the past week, the gas fees dropped to 10 gwei even for the high-priority transactions. One gwei is worth a billionth of an ETH meaning that a transaction on the Ethereum mainchain can be worth 50 cents in general.
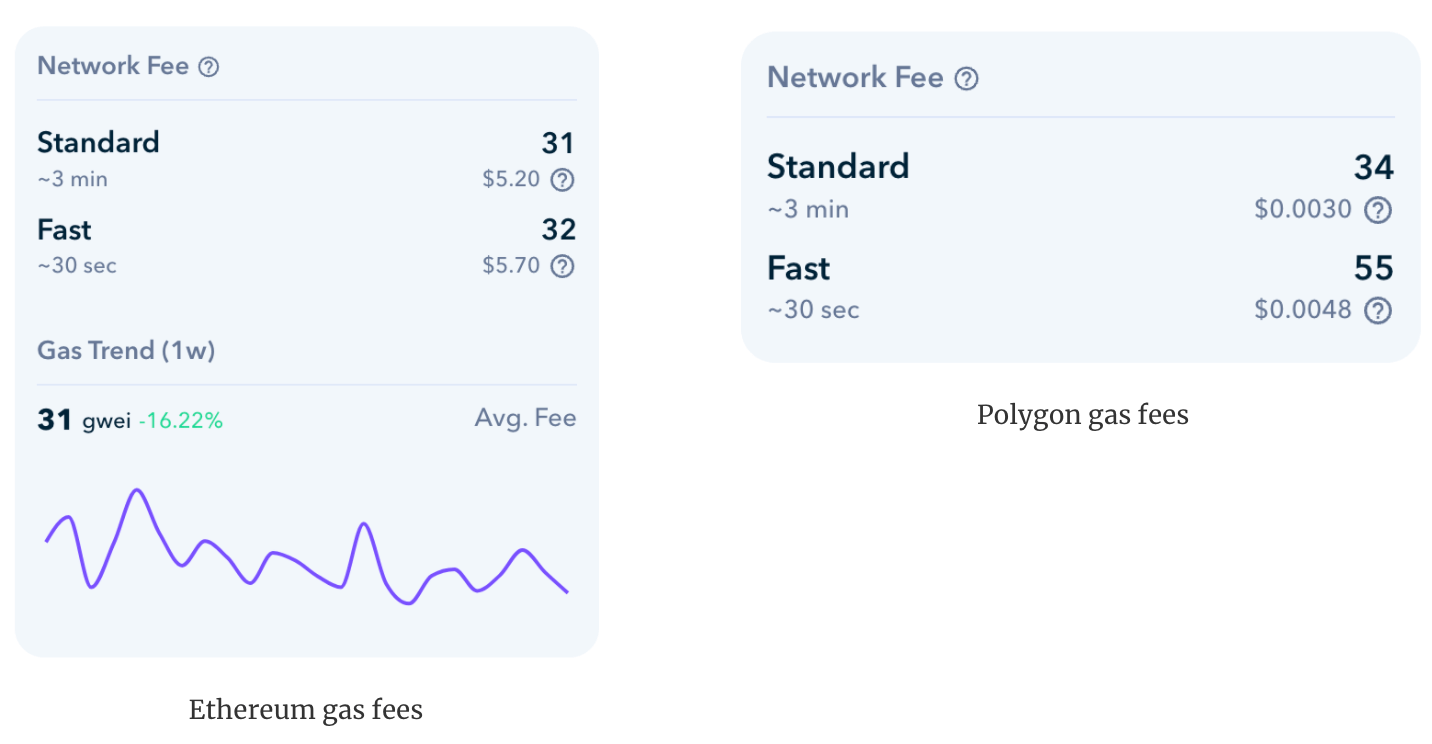
To enjoy such low price levels, you have to go back to July 2020. Thus, it is the first time in almost two years when using the ETH network’s layer-1 chain costs users very little. In May 2021, on the contrary, fees reached up to $70 per transaction. On May 19, 2021, an all-time-high gas fee was recorded at more than 659 gwei on average. That is nearly 66 times more than the 10 gwei recorded recently.
Related: Matic Launches Mainnet Aiming to Bring More ‘Firepower’ to Ethereum
Transactions Are Still High In Demand
But, network demand is still quite high with over one million transactions per day. The number did not fall as much as the gas fees, notably, the total number of transactions remains relatively level over time.
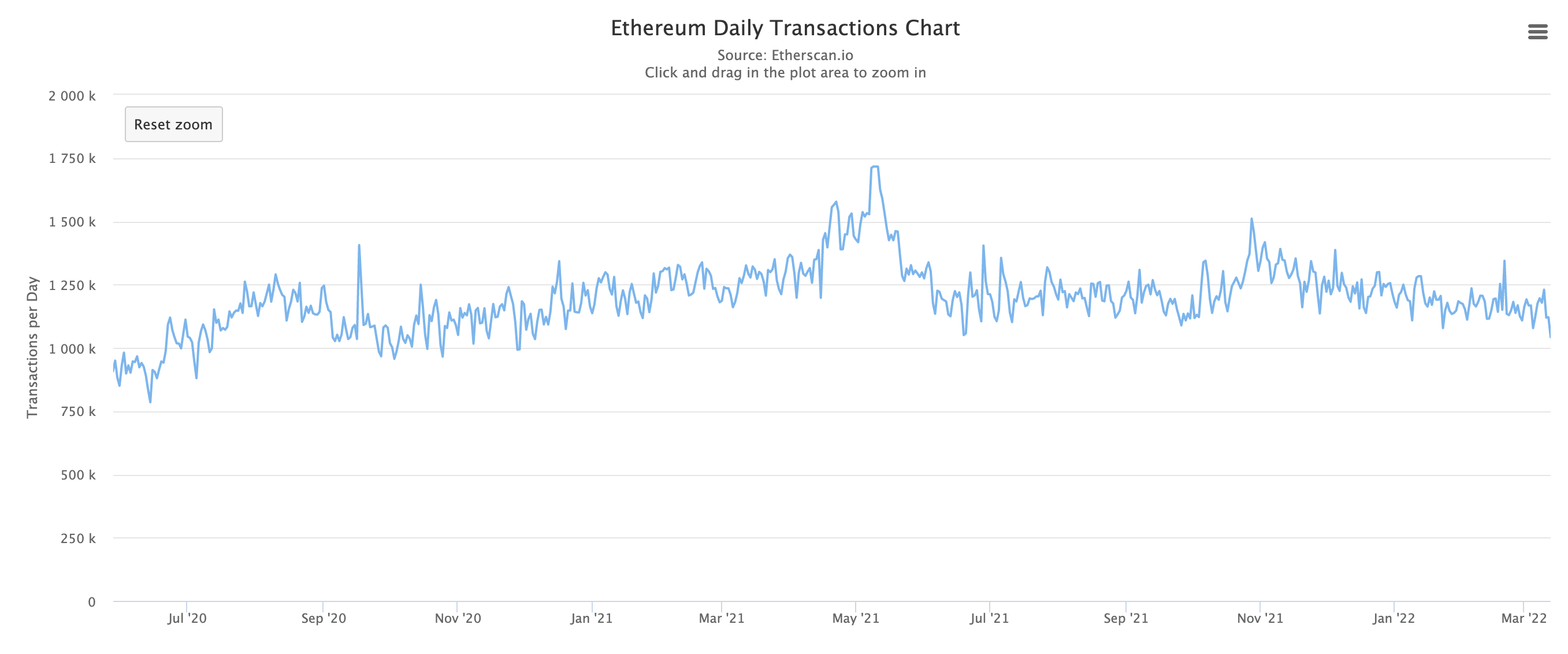
As reports emerged in the past week, the transaction fees on Ethereum have plummeted from as high as $200 to as low as $15 within the past six months. Based on Arcane Research, the main reason behind the recent plunge in Ethereum gas fees is the lower trading volume, and maybe lower interests, in NFTs.
Previously, NFT transfers accounted for a majority of the transactions happening on the Ethereum blockchain. But the abrupt drop in the interest levels in the past month has led to a major drop in the demand for the utilization of Ethereum.
To comprehend the relationship between the plunge in Ethereum’s gas fees drop and NFTs, one just has to look at how the trading volume on OpenSea dropped from $247 million to $124 million between February 1 and February 6. In that time, the median gas fee also plunged steeply from 134 gwei to 65 gwei.
Layer-2 Networks Gaining Popularity
The nonfungible token market appears to have cooled down since the last week of January. Based on market data from Nonfungible.com, the total number of sales is down from around 64,000 sales daily in mid-January to about 24,000 in mid-February.
In terms of dollars, the sales are down from $160 million on January 31 to $75 million in mid-February. Another reason that is believed to be behind the dropping gas fees may be the awakening of layer-2 networks and sidechains like Optimism, Polygon (MATIC), and Arbitrum.
Related: What Is The Polygon (Matic) Network And Why Is It Exploding In 2021?
These layer-2 networks are gaining popularity with up to 2.23 million ETH seen transacting on Arbitrum and other several other L2s. Furthermore, as all the fees no longer go to the miners, it might be that the implemented fee-burning mechanism set in motion with EIP-1559 mitigates network spam, mostly from the miners and other unwarranted actors.
In general, the low levels of Ethereum gas fees mean that the second-biggest blockchain by market capitalization is now more affordable to use than the Polygon sidechain. However, it is worth noting that Polygon decided to deliberately add 30 gwei to all the transactions to minimize spam activities. Thus, as long as this policy remains active, Ethereum’s gas fees will be comparable to Polygon’s fees and in some cases, they will be lower.
Binance Suspended Polygon Deposit And Withdrawal To Sync Nodes
According to Polygon, the temporary suspension by Binance was initiated to upgrade and synchronize the nodes, since the bug issue that affected Polygon was already resolved and the network is stable. Binance, the world’s largest cryptocurrency exchange by trading volume, said on March 15 that it would temporarily stop withdrawals and deposits for the Polygon Network.
This announcement came after the Polygon network’s outage since Friday after experiencing a network upgrade. The cryptocurrency exchange said that it would eventually reopen the withdrawal and deposit features once the network stabilizes.
Polygon network currently boasts millions of users and an evolving ecosystem. The network experienced an important upgrade on one of the three layers on March 11. However, due to a suspected bug, these layers never reached a consensus post the upgrade, resulting in downtime.
The Polygon developer account on Twitter confirmed that the bug had been resolved and the network is stable once more. It also confirmed that Binance is upgrading its nodes and syncing data, causing the temporary suspension.
Polygon PoS network is stable, and working fine. All funds are safe. Binance is upgrading its nodes, and currently syncing the block data, hence they have paused the deposit and withdrawal.https://t.co/hnhXp3AWga
— Polygon Devs 📍 DevX Global Tour (@0xPolygonDevs) March 15, 2022
The Polygon network comprises three layers, each of which has a distinct purpose. The Bor layer helps in generating blocks while the Ethereum layer runs smart contracts.
Related:Kine Protocol to Integrate with Polygon Network to Provide High-Speed Dependable Derivatives Trading
Heimdall is the third layer that had all the faults resulting in last week’s outage. The suspected bug made various Heimdall validators operate on different versions of the chain. That resulted in the general network not reaching 2/3 consensus.
While the outage for several hours was expected and was confirmed by the Polygon team, that 11-hour extended outage became a major reason for worries for most projects and traders. The Polygon developers fixed another upgrade in December 2021 after a security partner noted the existence of a vulnerability that may have put up to $24 billion worth of funds at risk.
Looking at the latest Polygonscan data, the network seems to have begun producing timely blocks, and the developers assured that the network bug issue has been resolved.
In 2021, the Matic Network was rebranded to Polygon. After the rebranding, it came with an expanded mission. Moving above its original branding as an Ethereum scaling solution, the network today refers to itself as an ‘internet of blockchains’ for Ethereum.
However, with multiple challenges experienced in recent months, it shows that the sidechain has some way to go before it becomes the ideal bridging solution.








