The financial world has been affected by many forms of criminal activities. In the current world, two of these criminal activities have proven persistent and more people keep falling for the fake offers. Ponzi and pyramid schemes account for significant losses among unsuspecting investors.
Both schemes lure in unsuspecting investors with enticing yet deceitful promises, ultimately leaving most participants grappling with substantial financial setbacks. To protect themselves from these financial hiccups, individuals have to understand the differences between these fraudulent tactics.
What Is A Ponzi Scheme?
This fraudulent investment program called a Ponzi scheme entices unsuspecting investors with the promise of delivering significantly high profits.
The Ponzi scheme was named after Charles Ponzi, who was popular in the early 20th century for using this strategy. It works on a deceptive foundation, where the returns that are paid to the earlier investors come not from any profits but from the investments of new participants.
These schemes depend on a constant infusion of new investors to support the promised payouts since they do not have a legitimate underpinning of commercial activity.
Ponzi schemes are unpopular since they lack transparency, often giving vague and inaccurate information about how they operate. The schemes are eventually unviable and they collapse after the flow of new investors decreases, leaving most investors with massive losses. Ponzi schemes are illegal in many jurisdictions because of their fraudulent character, and authorities actively pursue them to protect investors from any financial harm.
One of the most famous Ponzi schemes in the financial industry was set up by Bernie Madoff. Bernie Madoff’s infamous Ponzi scheme, uncovered in 2008, involved running a fake investment company that promised substantial and steady returns to clients while using new investments to pay off earlier investors.
Madoff deceived his investors by pretending to be a legitimate investment firm and promised consistent, large profits. Instead of investing money from previous investors, he used extra investments as leverage to pay rewards to the investors.
He created fake financial statements for years to maintain the appearance of success in the scheme. Because of the scheme’s final collapse during the global financial crisis, many investors suffered massive losses, and one of the largest financial frauds in history was exposed. Later on, Madoff was detained, found guilty, and handed a 150-year prison term for his role in running that mega-billion Ponzi fraud.
Ponzi Schemes In Cryptocurrency
Ponzi schemes have infiltrated the crypto space, targeting the attraction of quick rewards in the nascent market.
Some of the notable crypto Ponzi schemes include PlusToken, a major hoax that deceived many Asian investors out of billions of dollars. On the other hand, Bitconnect, a lending platform that imploded in 2018, also went under with investors’ crypto funds.
These incidents underscore the importance of exercising caution and skepticism in the cryptocurrency market, as the allure of quick profits can sometimes obscure malicious intentions. Thus, investors must learn to recognize red flags to protect themselves from fraudulent schemes.
Normally, the schemes lack transparency about their investing strategies and make significantly high-return promises, often with guarantees. They mostly rely majorly on referral networks, exert pressure on investors to move fast, and avoid regulatory audits and inspections.
Related: Op Ed: Beware Web3 – The Wild West Has Gone Online
What Is A Pyramid Scheme?
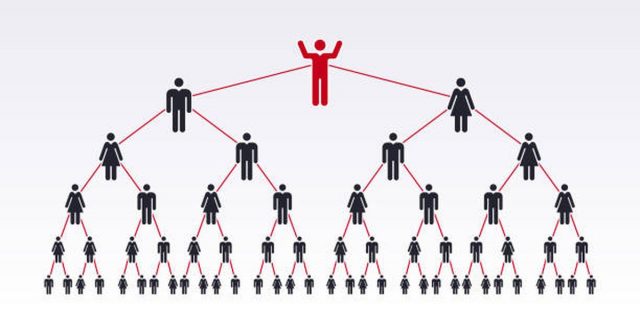
A pyramid scheme is described as a dishonest investment plan that dupes people into investing with claims of massive profits, normally by recruiting new participants.
People involved in a pyramid scheme have to make an initial financial investment, and instead of engaging in genuine product or service sales, their main emphasis is on convincing others to become a part of the scheme.
A hierarchical pyramid model is developed by the recruits’ responsibility to onboard recruits, who will also bring in more participants. Early participants normally get payments for their profits from later investors, which gives a false appearance of prosperity.
As it becomes harder to get new partners to support the ever-growing pyramid, the pyramid schemes become unsustainable and they are doomed to fail. Those at the top benefit when the schemes collapse, at the expense of those lower down the hierarchy who lose all their investments.
Because of their exploitative nature and the harm they inflict on innocent investors who fall prey to them, pyramid schemes are banned in most nations and jurisdictions. Pyramid schemes go for the same model as multi-level marketing (MLM). However, MLM participants can make commissions from the sale of the products and from recruiting new members.
On the contrary, legitimate services or products are often absent from the pyramid schemes, and the focus is on recruiting new members without providing any real value.
The Telexfree case serves as a prime example of a financial industry pyramid scheme. Operating from 2012 to 2014, Telexfree claimed to offer internet phone services, but its primary focus was on recruiting participants. Investors were enticed by the prospect of substantial profits in return for posting internet ads and bringing in new members. This deceptive scheme ultimately deceived thousands of individuals before its collapse.
Pyramid Schemes In Crypto
Unfortunately, pyramid schemes have entered the crypto space, targeting investors seeking rapid wealth gain in the nascent market.
Pyramid schemes often raise red flags since they promise extraordinarily high returns and emphasize recruiting new participants instead of offering real goods or services. The perpetrators of crypto pyramid schemes mostly give general or ambiguous details about their methods of return generation or investing plans. Nonetheless, because of the volatility experienced by digital assets, there are no guarantees in the world of cryptos. Any investment that promises profits has to be avoided.
There are no genuine services or products offered in pyramid scams. Instead of real business operations, recruitment and investments make up most of the scheme’s revenue. Moreover, the pyramid schemes might offer some complicated compensation plans that are highly challenging to understand. If one finds it hard to understand how the strategy generates profits, one needs to proceed cautiously.
Related: Why Did KuBitX’s African Crypto Exchange Startup Fail?
An infamous instance combining Ponzi and pyramid schemes is OneCoin, which operated between 2014 and 2017. It was presented as a state-of-the-art digital currency leveraging advanced blockchain technology, although it lacked transparency and authentic blockchain functionalities. The primary goal of the scheme was to allure new participants with substantial rewards, encouraging them to invest in OneCoin packages and recruit others.
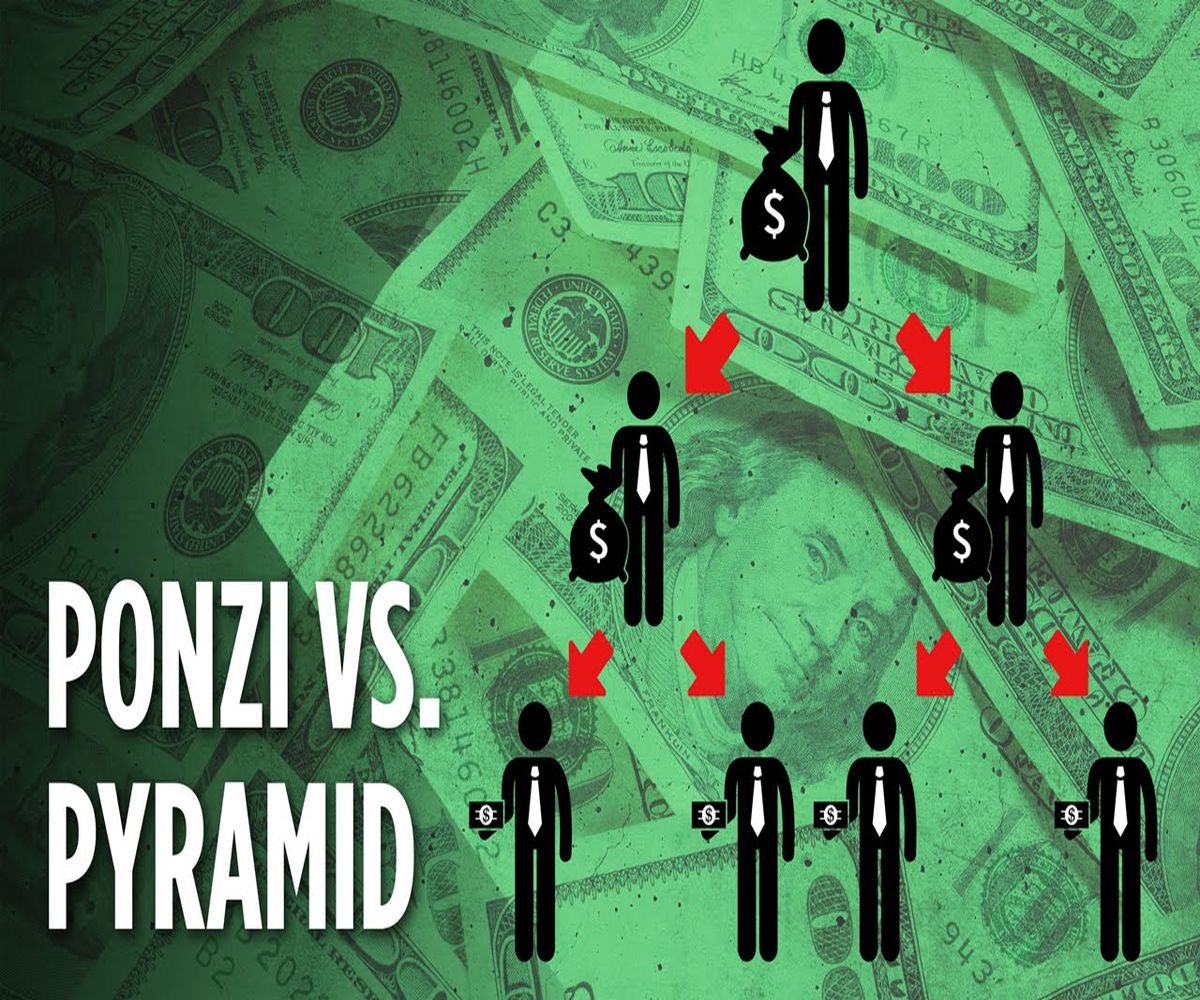
Ponzi vs. Pyramid Schemes
Both of these schemes defraud investors by making appealing but false promises, and most participants eventually suffer huge financial losses.
Investors can protect themselves from fraudulent schemes by comprehending their differences. Here are the main differences between these schemes:
- In the Ponzi scheme, a central figure attracts investors while in pyramid schemes the investors recruit others.
- The structure is a centralized hierarchy in the Ponzi schemes, while in the pyramid schemes it features hierarchical recruitment.
- The Ponzi schemes give profits from the funds supplied by the new investors while pyramid schemes rely on the investments from recruits.
- Ponzi schemes promise high and consistent returns on investments while pyramid schemes promise high, guaranteed returns through recruitments.
- Both of these schemes are unsustainable since they rely heavily on new recruitments.